mongo查询严格要求数据格式!
1、只想查出某些数据,不想全部数据都查出来
mysql:select name from user;
mongo:
db.user.find(
{},
{
_id : 0,
name : 1
}
)
说明:user是集合的名称,find里面两个{},第一个留空是想所有数据都查出来,加条件的话类型mysql的where,第二个{}表示的意思
类似mysql后面的select部分,0代表不显示,1代表显示。
2、分页查询
mysql:select * from user limit 0,10;
mongo:db.user.find({}).skip(0).limit(10)
说明:mongo的skip和limit与mysql同理,mysql的limit第一个参数是跳过的数据量与mongo的skip类似,比如第三页的数据是从
20开始的,mysql:limit 20,10,即:limit (page-1)*size,size
3、条件查询
mysql: select name from user where id = 1;
mongo: db.user.find( { id : 1 }, { name : 1 } )
说明:由于有严格要求数据格式,若存到mongo的id是字符串格式的话,查询的条件得加上双引号""
4、范围查询
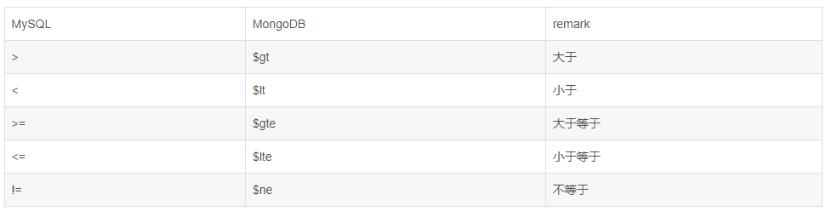
mysql:select name from user where id > 1 and id < 10;
mongo:
db.user.find(
{
id : {
$gt : 1,
$lt : 10
}
},
{ name : 1 }
)
说明:mysql的between其实就是>=和<=,字符串的话用范围查询好像会有问题,慎用!
5、in查询
mysql:select name from user where id in (1,2);
mongo:
db.user.find(
{
id : {
$in : [1, 2]
}
},
{ name : 1 }
)
说明:not in查询就把in换成in换成nin
6、条件统计count
mysql:select count(*) from user where id > 1;
mongo:
db.user.find(
{
id : {
$gt: 1
}
}
).count()
7、all查询
mongo可以将数组存储起来,若想查询某个字段(是个数组)同时包含值a和b
db.user.find(
{
detail: {
$all : ["7", "8"]
}
}
)
说明:这个查询的结果集,detail字段同时包含字符串7和字符串8
8、exists查询
比如我想找出所有包含字段name_real的结果集
db.user.find(
{
name_real : {
$exists : true
}
}
)
说明:上面查询的结果中,所有数据肯定都包含有name_real字段;改成false的话就变成不包含
9、is null查询
mysql:select * from user where age is null;
mongo:
db.user.find(
{ age : null }
)
但是这样会有问题,这个查询会把那些没有age字段的结果也查出来,结合exists优化下
db.user.find(
{
age: {
$in : [null],
$exists : true
}
}
)
查询is not null
db.user.find(
{
age: {
$ne : null,
$exists : true
}
}
)
10、取模运算
mongo提供取模运算,比如存储了一些数据,我想查出那些取模后等于某个值的数据可以使用$mod
比如下例查询年龄是10的倍数的用户
mysql:select * from user where age % 10 = 0;
mongo:
db.user.find(
{
age:{
$mod : [ 10 , 0 ]
}
}
)
11、查询数据元素个数
由于mongo可以存储数组,如果想查询数组中只有两个元素的记录时,可以使用$size
比如下例查询有三个兴趣爱好的用户
db.user.find(
{
favorite: {
$size: 3
}
}
)
12、正则匹配查询
如果想用正则匹配查询,可以使用$regex
比如下例匹配年龄是10以下的用户
db.user.find( { age: { $regex: /^([1-9])$/ } } )
13、只取一部分数据
类似mysql的limit,mongo也可以只取一部分数据
mysql:select * from user limit 10; mongo:db.user.find().limit(10)
14、排序
MySQL MongoDB 说明,asc 1 升序,desc -1 降序
mysql: select * from user order by age asc;
mongo: db.user.find().sort( {age: 1} )
说明:mongo字符串类型的也可以排序
15、求和
直接累加求和某一项
比如下例对年龄进行求和
mysql:select sum(age) as total from user;
mongo:
db.user.aggregate([
{
$group:
{
_id: null,
total: {
$sum: "$age"
}
}
}
])
分组求和
下例为按类型分组并求和
mysql: select type,sum(age) as total from user group by type;
mongo: db.user.aggregate([ { $group: { _id: "$type", total: { $sum: "$age" } } } ])
多条件分组求和
下例为按多个条件进行分组并求和
mysql: select type,sex,sum(age) as total from user group by type,sex;
mongo: db.user.aggregate([ { $group: { _id:{ type: "$type", sex: "$sex" }, total: { $sum: "$age" } } } ])
16、分组后having
下例为按条件分组并筛选出求和后大于100的数据
mysql: select type, sum(age) as total from user group by type having total > 100;
mongo: db.user.aggregate([ { $group: { _id: "$type", total: { $sum: "$age" } } }, { $match: { total: { $gt: 100 }}}])
17、条件分组
类似mysql的where+group by进行查询
下例为查找出2020-01-01(timestamp:1577808000)后注册的用户,并按类型分组求和
mysql:select type,sum(age) as total from user where created > 1577808000 group by type;
mongo:
db.user.aggregate([
{
$match: {
created: { $gt: 1577808000 }
}
},
{
$group: {
_id: "$type",
total: { $sum: "$age" }
}
}
])
条件分组并having筛选
下例为查找出2020-01-01(timestamp:1577808000)后注册的用户,并按类型分组,同时筛选出大于100的数据
mysql:select type,sum(age) as total from user where created > 1577808000 group by type having total > 100;
mongo:
db.user.aggregate([
{
$match: {
created: { $gt: 1577808000 }
}
},
{
$group: {
_id: "$type",
total: { $sum: "$age" }
}
},
{
$match: {
total: { $gt: 100 }
}
}
])
18、unwind
加入你的mongo的每一条记录有一个字段,存的是一个数组,数组里面是对象,类似这样,article字段含有
[
{ "uid" : 1, "title" : "XXX", "content" : "XXX", "views" : 10 },
{ "uid" : 2, "title" : "XXX", "content" : "XXX", "views" : 11 },
{ "uid" : 3, "title" : "XXX", "content" : "XXX", "views" : 12 }
]
使用unwind可以使上面原本一条记录进行展开,分为三条数据进行展示,有点像mysql的join查询,只不过mysql得分开两个表存
mysql:
select * from user as u left join article as a on (u.id=a.uid);
mongo:
db.user.aggregate([
{ $unwind: "$article" }
])
unwind后求和
mysql: select sum(views) as total from user as u left join article as a on (u.id=a.uid)) as data
mongo: db.user.aggregate([ { $unwind: "$article" }, { $group: { _id: null, total: { $sum: "$article.views" } } } ])
19、分组后统计总共有多少组
下例分按类型分组,并统计总数
mysql:select count(*) from (select type from user group by type);
mongo:
db.user.aggregate([
{
$group: {
_id: "$type"
}
},
{
$group:
{
_id : null,
count: { $sum: 1 }
}
}
])
20、aggregate类型linux的grep指令,像管道处理一样,一级接一级,比如:筛选、分组、过滤等,最后返回结果
db.user.aggregate([
{ $match: { sex: "boy" } },
{ $group: { _id: "$type", total: { $sum: "$age" } } }
])
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/xiaogxiao/article/details/115695457